
However, even though the open access dataset provided was acquired from many participants (twenty-nine) 37, we could not fully reflect a variety of experimental paradigms due to time constraints of the experiment. In addition, basic data processing methods for the EEG-NIRS open access dataset were given as a reference not only for hybrid BCI beginners but also experts. Our group has released an open access dataset for a hybrid EEG-NIRS BCI 37, which includes datasets for left- and right-hand motor imagery, mental arithmetic, and several types of motion artifacts.

Moreover, the quality and characteristics of open datasets can be validated by many researchers and thus more credible and reproducible results can be obtained. Furthermore, using an identical dataset allows convenient comparison of data processing methods and validation/benchmarking of newly proposed methods. Generally, open access datasets can save a considerable amount of time for researchers, especially when repetitive data recordings and many participants are required 36. Hybrid EEG-NIRS brain-imaging techniques are extensively investigated however, so far, the corresponding datasets are rarely released for use by other research groups-in contrast to EEG datasets 31– 35. EEG-NIRS correlation analyses helped further to reveal the intricate relationship between electrophysiological and hemodynamic changes in neuroscience 30. For example, hybrid EEG-NIRS BCI systems showed better classification accuracy than each unimodal BCI system 26, 27, and EEG-NIRS hybrids were also used to better understand the linguistic functions of newborns and infants 28, 29. EEG-NIRS hybrids have proven their merit in a variety of research fields 19– 23. For this purpose, new hybrid instrumentations have also been developed from hybrid tabletop devices into miniaturized wearable instruments 24, 25. Over the last decade, an increasing number of research approaches have focused on the use of simultaneously acquired EEG and NIRS. NIRS is suitable for simultaneous and artifact-free recording with EEG because its near-infrared light does not interfere with the electrical EEG measurement 4. Recently, simultaneous EEG and NIRS systems, so-called hybrid systems, have been gaining more attention 19– 23. NIRS is more robust when confronted with electrical noise and motion-based muscle activity artifacts than EEG 18 therefore, it can be a viable alternative to EEG in a noisy environment. On the other hand, near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a promising tool for monitoring metabolic changes in the brain with good spatial but low temporal resolution due to the inherent hemodynamic delay 16, 17. EEG measures the neural activities with an excellent temporal resolution (within a millisecond range), but suffers from poor spatial resolution due to volume conduction, thereby resulting in resolution limits in source localization 15. EEG is the most popular electrophysiological method widely used in many research areas such as neuroscience, neural rehabilitation, and brain-computer interface (BCI) 5– 14. Apart from invasive methods (e.g., electrocorticography), non-invasive functional imaging methods can be mainly categorized into 1) electrophysiological methods and 2) metabolic methods 4. Brain-imaging technologies fall into two broad categories: 1) structural imaging, such as computed tomography (CT) and 2) functional imaging, such as electroencephalography (EEG). There have been considerable advances in brain-imaging technologies over recent years 1– 3. We expect that the dataset provided will facilitate performance evaluation and comparison of many neuroimaging analysis techniques. For the WG task (dataset C), the EEG spectral power and spatiotemporal characteristics of hemodynamic responses are analyzed, and the potential merit of hybrid EEG-NIRS BCIs was validated with respect to classification accuracy. Spatiotemporal characteristics of hemodynamic responses are also shown.
Time-frequency analysis was performed to show the EEG spectral power to differentiate the task-relevant activations.
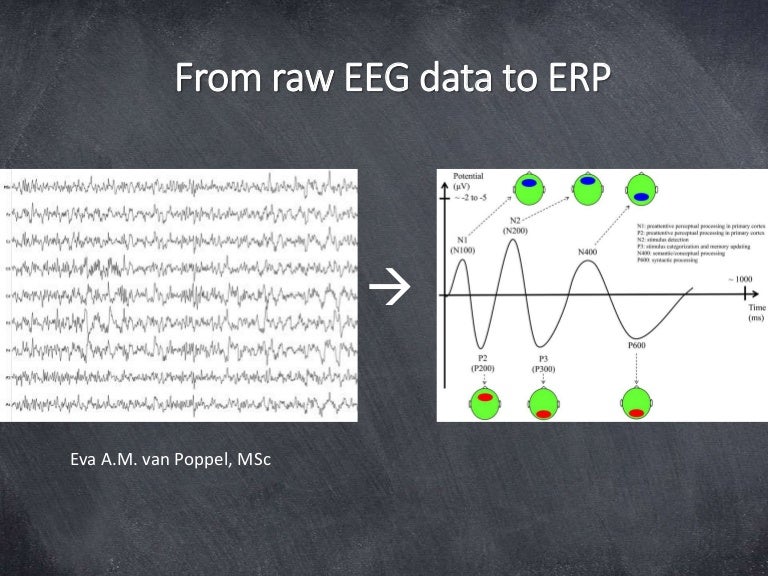
For n-back (dataset A) and DSR tasks (dataset B), event-related potential (ERP) analysis was performed, and spatiotemporal characteristics and classification results for ‘target’ versus ‘non-target’ (dataset A) and symbol ‘O’ versus symbol ‘X’ (dataset B) are provided. The data provided includes: 1) measured data, 2) demographic data, and 3) basic analysis results. Twenty-six healthy participants performed three cognitive tasks: 1) n-back (0-, 2- and 3-back), 2) discrimination/selection response task (DSR) and 3) word generation (WG) tasks. We provide an open access multimodal brain-imaging dataset of simultaneous electroencephalography (EEG) and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) recordings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
